Pregnancy and dental diseases
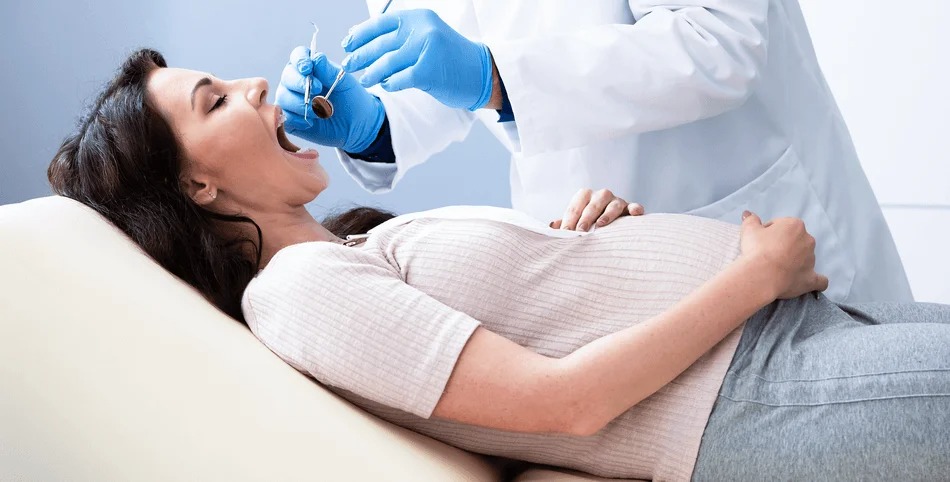
are an important topic as pregnancy affects oral and dental health, and vice versa, dental problems can affect the health of the mother and fetus. During pregnancy, hormonal changes increase blood flow to the gums, causing swelling and bleeding, especially if oral care is neglected. High hormone levels may also cause oral thrush appearing as white spots, increase tooth sensitivity, and cause enamel erosion due to vomiting and acid reflux, leading to tooth decay.
Care and prevention include regular dental check-ups, adopting a healthy diet, avoiding smoking, using a soft toothbrush with fluoride toothpaste, and regular flossing to reduce risks.
Dental treatment during pregnancy is recommended to avoid the first trimester unless necessary; the second trimester is preferred for urgent treatments. Local anesthesia is generally safe, and antibiotics like penicillin can be used, but tetracycline is contraindicated due to its effect on fetal teeth development.
Untreated gum and dental problems are linked to an increased risk of premature birth or low birth weight, making timely dental care essential for the health of both mother and baby.
In summary, pregnancy causes multiple dental issues due to hormonal changes. Maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and careful management of dental problems during pregnancy are critical to prevent complications and safeguard maternal and fetal health.







.jpg)